Common Hazards on Construction Sites and How to Mitigate Them
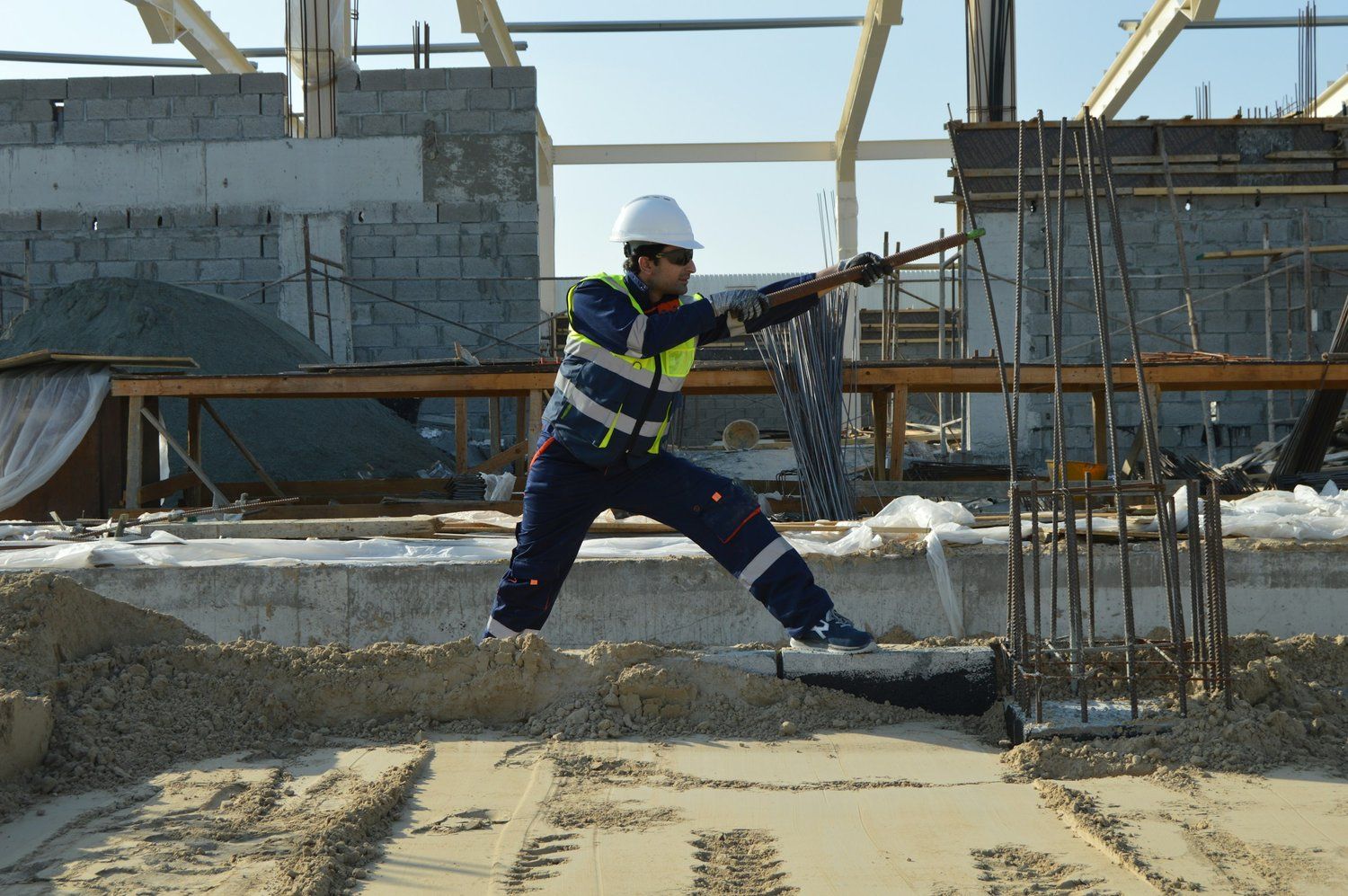
Construction sites are inherently risky environments, presenting a variety of hazards to workers and bystanders alike. From falls and machinery accidents to exposure to hazardous substances, the potential for injury is significant. However, with proper safety measures and awareness, many of these risks can be effectively mitigated. Here, we discuss some of the most common hazards found on construction sites and the strategies to manage and reduce them.
1. Falls from Heights
Hazard: Falls from heights are one of the leading causes of fatalities in the construction industry. Workers are often required to operate at elevated heights on scaffolds, ladders, or roofs, increasing the risk of falls.
Mitigation:
-
Use of Guardrails: Install guardrails on all open sides of platforms, scaffolds, and around open holes.
-
Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS): Equip workers with harnesses and ensure they are securely tied off to anchor points.
-
Training and Supervision: Provide training on the proper use of fall protection equipment and ensure constant supervision.
2. Struck-by Incidents
Hazard: Workers can be struck by moving vehicles, falling objects, or equipment, leading to serious injuries or fatalities.
Mitigation:
-
Protective Barriers: Use barriers, signs, and warning lines to keep unauthorized personnel out of danger zones.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensure all workers wear hard hats, high-visibility vests, and other necessary PPE.
-
Safe Work Zones: Establish and enforce exclusion zones for heavy machinery and vehicle operation.
3. Electrical Hazards
Hazard: Exposure to live wires, faulty equipment, or improper grounding can result in electrical shocks or burns.
Mitigation:
-
Proper Grounding and Insulation: Ensure all electrical tools and equipment are properly grounded and insulated.
-
Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Implement lockout/tagout procedures to ensure machinery is powered off and cannot be restarted during maintenance.
-
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections and maintenance of electrical equipment and systems.
4. Hazardous Substances
Hazard: Workers may be exposed to hazardous substances such as asbestos, lead, chemicals, or silica dust, which can lead to respiratory issues or other health problems.
Mitigation:
-
Proper Ventilation: Use ventilation systems to reduce the concentration of hazardous substances in the air.
-
Use of PPE: Provide appropriate PPE, including respirators, gloves, and protective clothing.
-
Substance Handling Training: Train workers on safe handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials.
5. Machinery Accidents
Hazard: Workers operating or working near heavy machinery are at risk of accidents caused by malfunctioning equipment or human error.
Mitigation:
-
Machine Guarding: Ensure all machinery has proper guarding to protect workers from moving parts.
-
Operator Training: Only trained and certified personnel should operate heavy machinery.
-
Routine Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance and safety checks on all machinery to ensure they are in proper working condition.
6. Slips, Trips, and Falls
Hazard: Slippery surfaces, uneven ground, and debris can cause workers to slip, trip, or fall, leading to injuries.
Mitigation:
-
Housekeeping: Maintain a clean and organized worksite, promptly clearing debris and spills.
-
Non-Slip Footwear: Ensure workers wear appropriate non-slip footwear.
-
Signage: Use signs to warn of slippery or uneven surfaces.
Conclusion
Safety on construction sites is paramount, and understanding common hazards is the first step in creating a safer work environment. By implementing comprehensive safety measures, conducting regular training, and fostering a culture of safety, many construction site accidents can be prevented. Employers and workers must work together to identify potential hazards and take proactive steps to mitigate them, ensuring everyone on site returns home safely.
Most Popular Greenhouse Articles