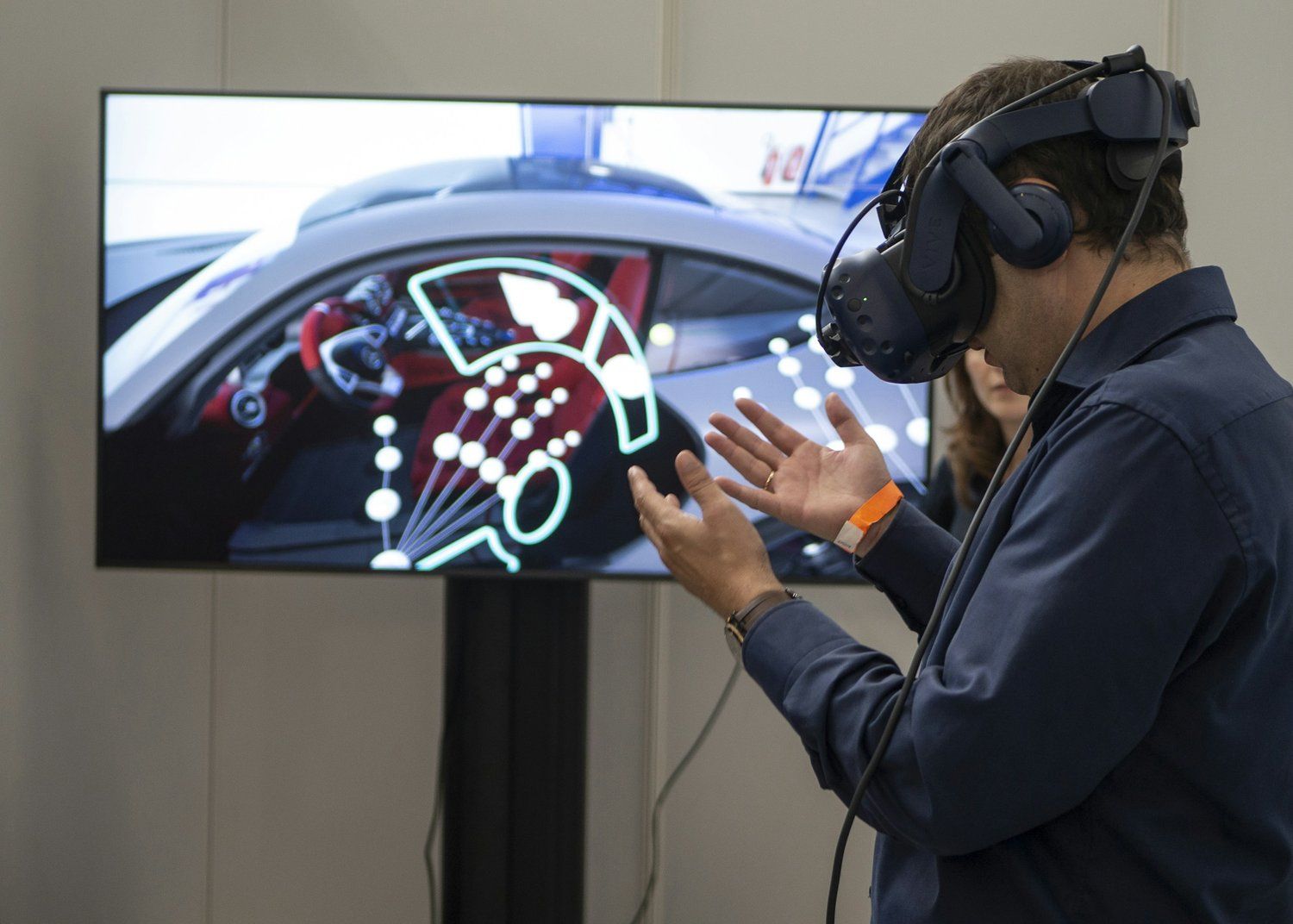
Understanding Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
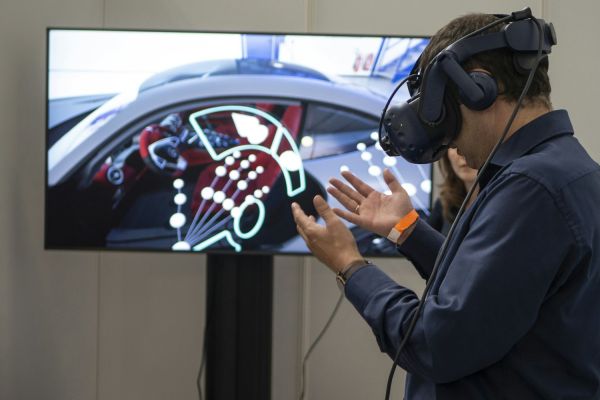
Virtual Reality (VR) creates fully immersive, computer-generated environments that users can interact with as if they were physically present. In construction, VR allows stakeholders to experience a project in a simulated environment before it’s built. Architects, engineers, and clients can walk through virtual buildings, exploring every detail from different angles and perspectives. This immersive experience aids in visualizing spatial relationships, identifying design flaws early on, and making informed decisions about materials and layouts.
Augmented Reality (AR), on the other hand, overlays digital information onto the real world through devices like smartphones or AR glasses. In construction, AR enhances the physical environment by superimposing digital models, data, and instructions onto the actual construction site. This technology enables on-site workers to see detailed 3D models of structures, utilities, and infrastructure elements directly in their field of view. AR can also provide real-time data, such as progress updates, safety hazards, and equipment locations, enhancing productivity and safety on site.
Benefits of VR and AR in Construction
-
Enhanced Visualization and Design Review: VR allows stakeholders to immerse themselves in a project, providing a better understanding of scale, proportions, and spatial relationships. It facilitates more comprehensive design reviews and enables early detection of clashes or design errors.
-
Improved Communication and Collaboration: AR enables real-time collaboration among teams by overlaying digital annotations and instructions onto physical objects. This enhances communication between architects, engineers, contractors, and clients, ensuring everyone is on the same page throughout the project lifecycle.
-
Efficient Project Planning and Management: VR simulations help project managers optimize workflows, plan logistics, and anticipate challenges before construction begins. AR assists on-site workers by providing access to critical information, reducing downtime, and improving productivity.
-
Cost and Time Savings: By identifying design issues early and streamlining communication, VR and AR can reduce costly rework and delays. These technologies also contribute to faster decision-making and more efficient resource allocation.
-
Enhanced Safety Training: VR can simulate hazardous construction scenarios, allowing workers to practice safety protocols in a controlled environment. AR provides real-time safety alerts and visualizations of potential hazards on site, minimizing risks and enhancing workplace safety.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
1. Design Visualization and Client Engagement: Architecture firms use VR to showcase design concepts to clients, providing a realistic preview of the final project.
2. On-Site Construction Assistance: Companies like Trimble and Autodesk have developed AR applications that guide construction workers with real-time instructions, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
3. Training and Skills Development: VR training modules are being used to educate workers on equipment operation, safety procedures, and complex construction tasks.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While VR and AR offer significant benefits to the construction industry, challenges such as initial costs, integration with existing workflows, and technological complexity remain. However, ongoing advancements in hardware, software, and connectivity are making these technologies more accessible and practical for construction firms of all sizes.
Looking ahead, the adoption of VR and AR is expected to continue growing as construction stakeholders recognize their potential to transform project delivery, improve collaboration, and drive innovation. As these technologies evolve, they will likely become indispensable tools in the modern construction toolkit, paving the way for smarter, safer, and more efficient building practices.
In conclusion, Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality are not just changing how buildings are designed and constructed—they are reshaping the entire construction ecosystem, from planning and execution to maintenance and beyond. Embracing these technologies represents a significant opportunity for construction professionals to stay competitive and lead the industry into a new era of innovation and efficiency.
Most Popular Greenhouse Articles