How Technology is Revolutionizing the Construction Industry
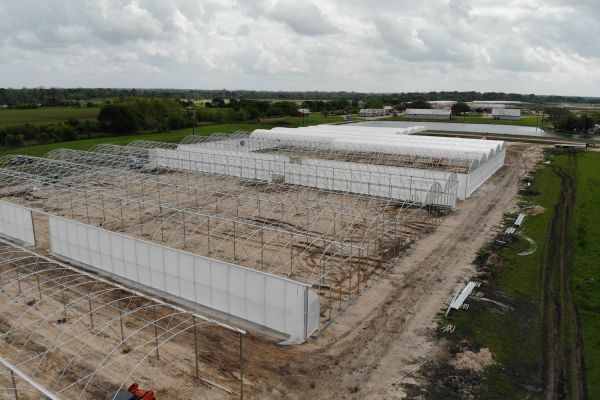
The construction industry, long known for its reliance on manual labor and traditional methods, is undergoing a significant transformation. The adoption of advanced technologies is reshaping how construction projects are planned, executed, and managed. These innovations are not only enhancing efficiency and productivity but also improving safety and sustainability. Here’s an in-depth look at how technology is revolutionizing the construction industry.
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
1.1 Enhanced Collaboration
-
Overview: Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of a building’s physical and functional characteristics. It provides a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility.
-
Impact: BIM allows architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate more effectively by providing a comprehensive view of the project. This reduces errors, improves decision-making, and streamlines the construction process.
1.2 Improved Visualization
-
Overview: BIM offers 3D visualization capabilities, enabling stakeholders to see the project in detail before construction begins.
-
Impact: Enhanced visualization helps in identifying potential issues early, improving planning and reducing costly modifications during construction.
2. Drones and Aerial Imaging
2.1 Site Surveys and Inspections
-
Overview: Drones are increasingly used for site surveys, inspections, and progress monitoring.
-
Impact: They provide real-time aerial footage and high-resolution images, enabling precise mapping and reducing the time and cost associated with traditional survey methods.
2.2 Safety Monitoring
-
Overview: Drones can be used to monitor construction sites for safety compliance and to identify potential hazards.
-
Impact: This enhances safety management by allowing for quick response to issues and reducing the risk of accidents.
3. Robotics and Automation
3.1 Robotic Construction
-
Overview: Robotics in construction includes automated bricklaying robots, 3D printing of building components, and robotic arms for material handling.
-
Impact: These technologies increase construction speed, precision, and efficiency while reducing labor costs and minimizing human error.
3.2 Autonomous Equipment
-
Overview: Autonomous construction equipment, such as excavators and bulldozers, can perform tasks without direct human control.
-
Impact: This equipment enhances productivity and safety by operating in hazardous environments and performing repetitive tasks with consistent accuracy.
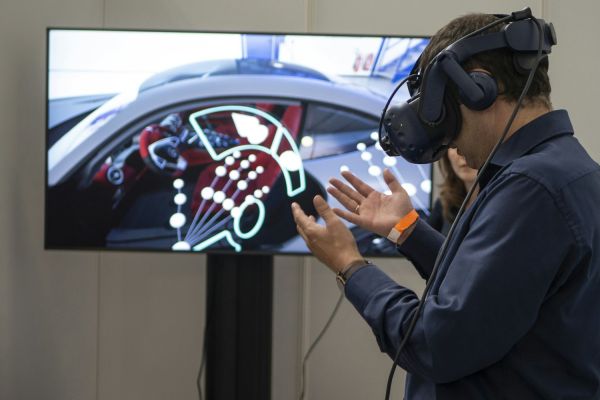
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
4.1 Design Visualization
-
Overview: AR and VR technologies enable immersive visualization of building designs and construction plans.
-
Impact: These technologies allow stakeholders to experience the building in a virtual environment, making it easier to spot design flaws and make necessary adjustments before construction begins.
4.2 Training and Safety
-
Overview: AR and VR can be used for training construction workers in a simulated environment.
-
Impact: This improves skills and safety by allowing workers to practice procedures and understand the site layout without being exposed to real-world risks.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
5.1 Smart Construction Sites
-
Overview: IoT involves connecting construction equipment and machinery to the internet, enabling real-time monitoring and data collection.
-
Impact: IoT enhances site management by providing insights into equipment performance, site conditions, and worker safety. This data can be used to optimize operations and prevent downtime.
5.2 Predictive Maintenance
-
Overview: IoT sensors can predict when equipment needs maintenance based on real-time data.
-
Impact: Predictive maintenance reduces unexpected breakdowns, extends the lifespan of equipment, and minimizes repair costs.
6. Advanced Materials
6.1 Innovative Building Materials
-
Overview: Advances in material science have led to the development of stronger, lighter, and more sustainable building materials.
-
Impact: Materials such as self-healing concrete, carbon fiber-reinforced composites, and aerogels improve building durability, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance energy efficiency.
6.2 Sustainability
-
Overview: The use of sustainable materials and green building techniques is becoming more prevalent.
-
Impact: These innovations reduce the environmental footprint of construction projects, promoting energy efficiency and reducing waste.
7. Construction Management Software
7.1 Project Management Tools
-
Overview: Construction management software integrates various aspects of project management, including scheduling, budgeting, resource allocation, and communication.
-
Impact: These tools improve project coordination, enhance transparency, and enable real-time decision-making, leading to more efficient project execution.
7.2 Document Management
-
Overview: Digital document management systems streamline the storage and retrieval of project documents.
-
Impact: This reduces the risk of lost or misplaced documents, improves compliance with regulatory requirements, and facilitates easier information sharing among stakeholders.
Conclusion
The integration of advanced technologies in the construction industry is driving a significant shift towards more efficient, safe, and sustainable building practices. From BIM and drones to robotics and IoT, these innovations are transforming every aspect of construction management and execution. Embracing these technologies not only enhances productivity but also positions construction firms to meet the demands of an increasingly complex and dynamic industry landscape.
For further insights into leveraging technology in your construction projects, don’t hesitate to reach out. Staying ahead of technological trends is key to maintaining a competitive edge in the construction industry!
Most Popular Greenhouse Articles