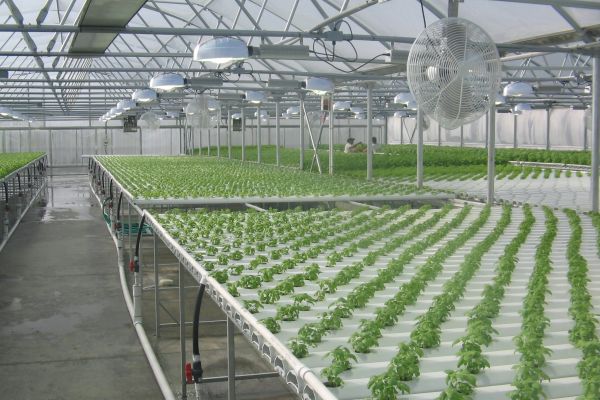
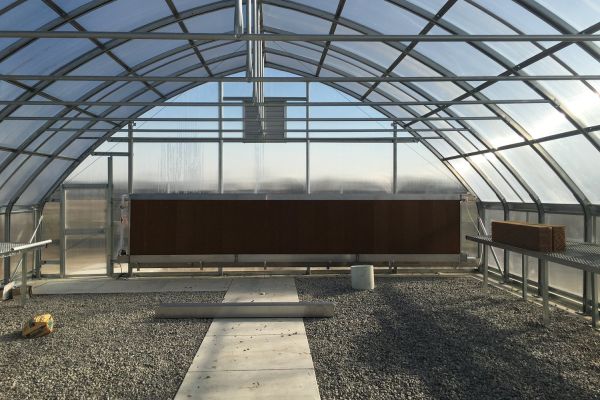
Trends in Commercial Agricultural Construction Design
The agricultural industry is undergoing significant transformations driven by technological advancements, sustainability concerns, and the need for increased efficiency. These changes are reflected in the design and construction of commercial agricultural facilities. Modern farms and greenhouses are now integrating innovative features to enhance productivity, reduce environmental impact, and meet the evolving demands of the market. Here are some of the key trends shaping commercial agricultural construction design today.
1. Sustainable and Green Building Practices
1.1 Energy Efficiency
-
Solar Power: Increasingly, agricultural facilities are incorporating solar panels to harness renewable energy, reducing reliance on conventional power sources and lowering operational costs.
-
Energy-Efficient HVAC Systems: Advanced heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems help maintain optimal indoor conditions while minimizing energy consumption.
1.2 Water Conservation
-
Rainwater Harvesting: Systems that capture and store rainwater for irrigation and other uses are becoming standard, especially in regions prone to water scarcity.
-
Efficient Irrigation Systems: Drip irrigation and automated watering systems ensure precise water delivery, reducing waste and improving crop health.
1.3 Eco-Friendly Materials
-
Recycled and Recyclable Materials: The use of recycled steel, sustainable wood, and other eco-friendly materials is gaining traction, promoting environmental stewardship.
2. Smart Technology Integration
2.1 IoT and Automation
-
Sensors and IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices monitor soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and other critical parameters, providing real-time data to optimize growing conditions.
-
Automated Systems: From climate control to irrigation, automation reduces labor costs and enhances precision in agricultural operations.
2.2 Data Analytics
-
Predictive Analytics: By analyzing data collected from various sensors, farmers can predict and respond to potential issues such as pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies.
-
Farm Management Software: Integrated software platforms manage everything from planting schedules to inventory, streamlining operations and improving decision-making.
3. Vertical and Urban Farming
3.1 Space Optimization
-
Vertical Farming: Stacking growing systems vertically maximizes space utilization, allowing for high-density crop production in smaller areas.
-
Hydroponics and Aeroponics: Soil-less growing methods such as hydroponics and aeroponics are ideal for urban environments, offering high yields with reduced resource inputs.
3.2 Urban Integration
-
Rooftop Greenhouses: Converting urban rooftops into productive greenhouses helps localize food production, reduce transportation costs, and promote urban sustainability.
-
Community Farms: Urban farms and community gardens foster local engagement, providing fresh produce and educational opportunities to urban populations.
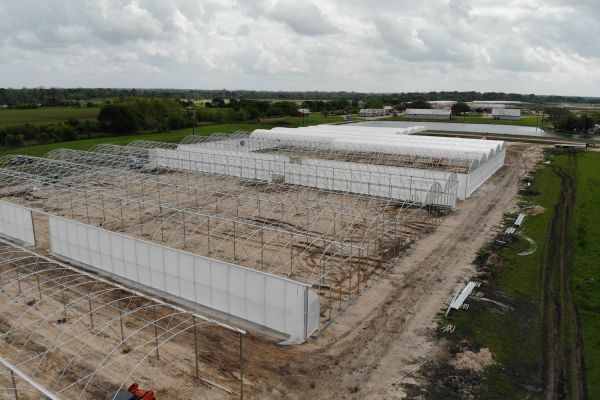
4. Modular and Prefabricated Structures
4.1 Flexibility and Scalability
-
Modular Design: Modular greenhouses and barns can be expanded or reconfigured easily, allowing farmers to scale operations in response to market demand.
-
Prefabricated Components: Prefabricated building elements reduce construction time and labor costs, enabling faster project completion and reduced downtime.
4.2 Cost-Effectiveness
-
Standardization: Prefabrication and modular construction standardize components, improving quality control and reducing waste.
-
Speed of Construction: Accelerated build times translate to quicker operational start-up and faster return on investment.
5. Focus on Worker Safety and Comfort
5.1 Ergonomic Design
-
Ergonomic Workspaces: Designing workspaces that minimize physical strain on workers helps improve productivity and reduce injury rates.
-
Safety Features: Incorporating safety features such as anti-slip flooring, handrails, and proper lighting enhances worker safety and reduces accident risks.
5.2 Health and Wellbeing
-
Ventilation and Air Quality: Advanced ventilation systems ensure a healthy working environment by maintaining air quality and reducing exposure to harmful substances.
-
Break Areas: Providing comfortable break areas and amenities for workers helps improve morale and overall job satisfaction.
Conclusion
The trends in commercial agricultural construction design reflect a broader shift towards sustainability, efficiency, and technological integration. By adopting these trends, agricultural businesses can enhance productivity, reduce environmental impact, and stay competitive in an evolving market. Embracing innovative design and construction practices is essential for the future of agriculture, paving the way for more resilient and sustainable food production systems.
Most Popular Greenhouse Articles