Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Commercial Greenhouse
Building a commercial greenhouse is a significant investment, but it can provide substantial rewards by extending growing seasons, increasing crop yields, and allowing for the cultivation of a diverse range of plants. This step-by-step guide will help you navigate the process of constructing a commercial greenhouse, from planning and site selection to the final touches.
Step 1: Planning and Design
1.1 Define Your Objectives
-
Determine what types of crops you plan to grow.
-
Consider your production goals, budget, and timeline.
1.2 Research Local Regulations
-
Check local zoning laws and building codes.
-
Obtain necessary permits and licenses.
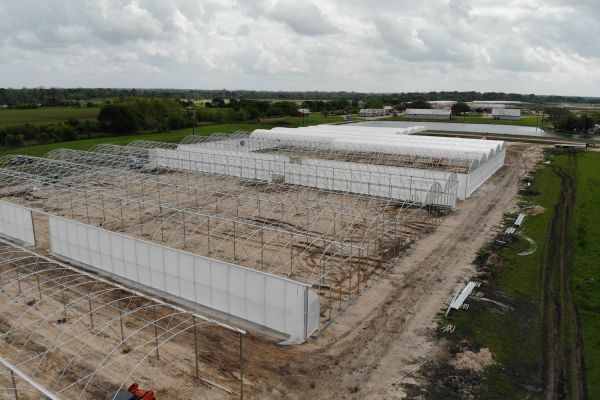
1.3 Choose the Greenhouse Type
-
Freestanding: Ideal for large-scale operations with space for expansion.
-
Gutter-Connected: Suitable for maximizing space efficiency and easier climate control in larger operations.
1.4 Design the Layout
-
Plan the internal layout, including the arrangement of benches, irrigation systems, and walkways.
-
Ensure adequate space for ventilation, heating, and cooling systems.
Step 2: Site Selection
2.1 Evaluate the Location
-
Select a site with good sunlight exposure, preferably with southern or southeastern orientation.
-
Ensure the site has proper drainage to prevent water accumulation.
2.2 Consider Accessibility
-
Choose a location with easy access to utilities (water, electricity) and transportation routes for the delivery of materials and produce.
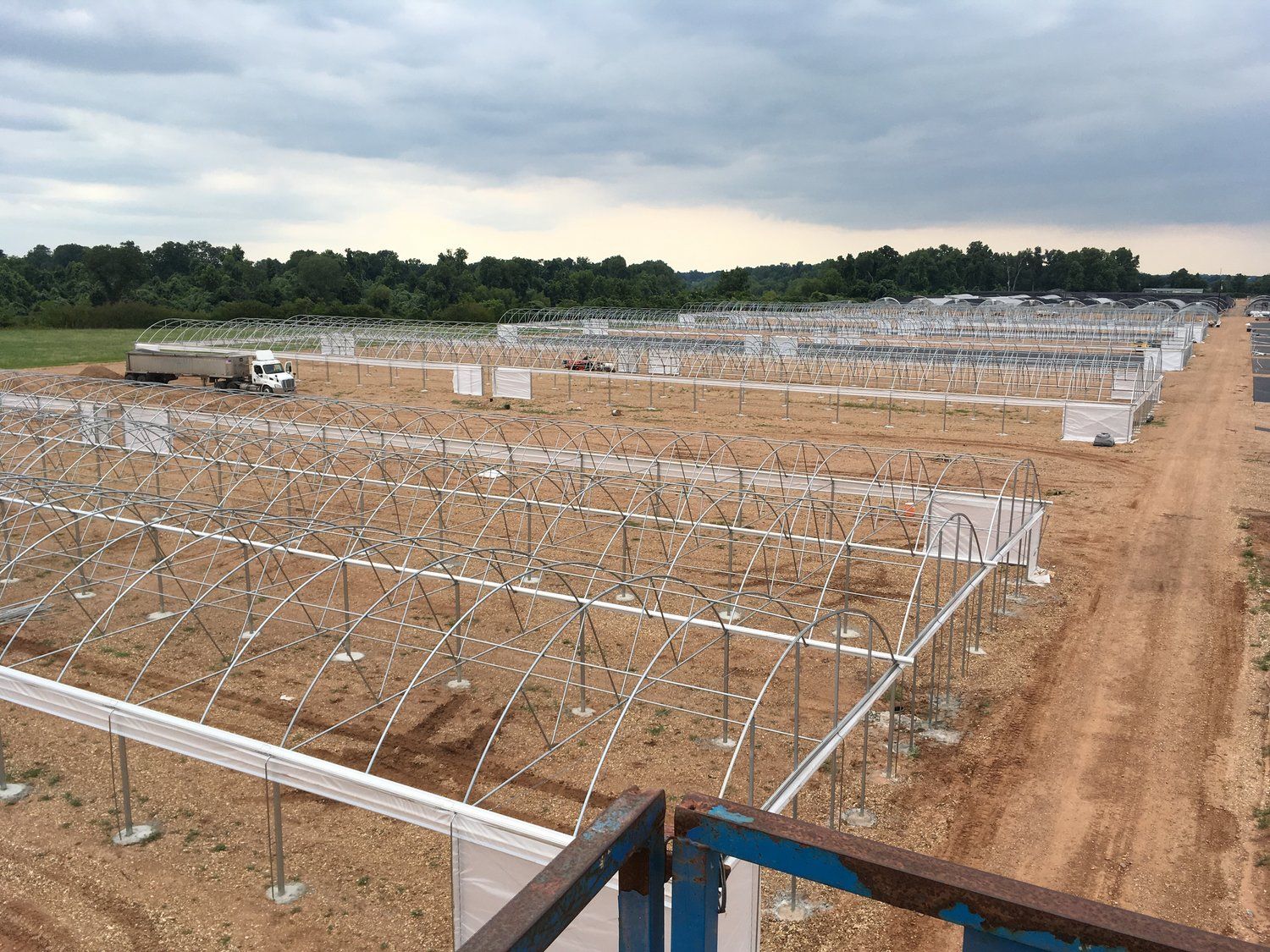
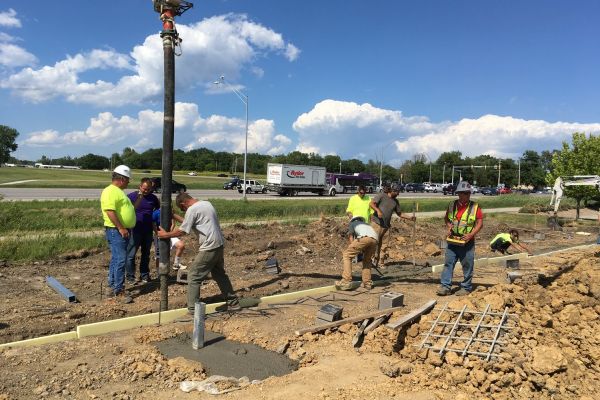
Step 3: Foundation and Structure
3.1 Prepare the Ground
-
Clear the site of debris and level the ground.
-
Install a drainage system if necessary to manage water runoff.
3.2 Lay the Foundation
-
Choose between concrete, gravel, or compacted soil foundations based on your greenhouse size and design.
-
Ensure the foundation is level and sturdy to support the greenhouse structure.
3.3 Build the Frame
-
Assemble the frame using materials such as galvanized steel, aluminum, or wood.
-
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for assembling the frame components.
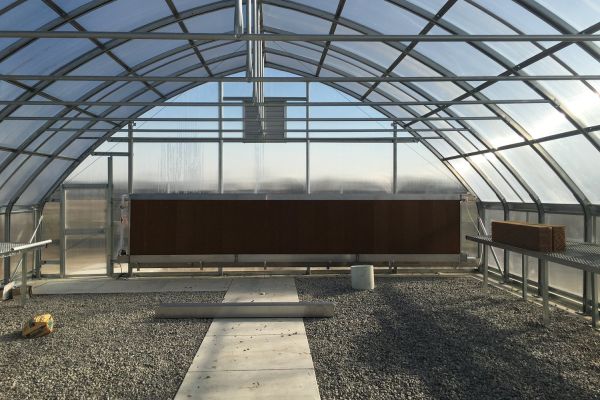
Step 4: Covering and Insulation
4.1 Select the Covering Material
-
Polyethylene Film: Affordable and easy to install, but requires regular replacement.
-
Polycarbonate Panels: Durable and provides excellent insulation.
-
Glass: High light transmission and long-lasting, but expensive and heavy.
4.2 Install the Covering
-
Secure the covering material tightly to the frame to ensure proper insulation and reduce heat loss.
-
Seal all joints and seams to prevent drafts.
Step 5: Climate Control Systems
5.1 Heating System
-
Choose a heating system suitable for your climate and greenhouse size (e.g., gas heaters, electric heaters, or radiant floor heating).
-
Install thermostats and sensors to regulate temperature automatically.
5.2 Ventilation and Cooling
-
Install exhaust fans, ridge vents, and roll-up sides to facilitate air circulation.
-
Consider using shade cloths or evaporative coolers for temperature regulation during hot weather.
5.3 Irrigation System
-
Set up an efficient irrigation system such as drip irrigation or overhead sprinklers.
-
Ensure even water distribution to all plants and incorporate timers for automated watering.
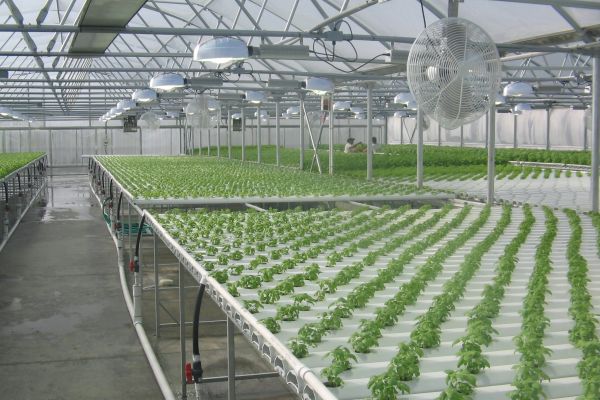
Step 6: Internal Layout and Equipment
6.1 Benches and Shelving
-
Install benches and shelving units to organize plants at different heights.
-
Use materials resistant to moisture and corrosion.
6.2 Lighting
-
Install supplemental lighting if natural sunlight is insufficient for your plants’ needs.
-
Choose energy-efficient LED lights to reduce electricity costs.
6.3 Fertilization and Pest Control
-
Set up a fertilization system, such as fertigation, to deliver nutrients directly through the irrigation system.
-
Implement integrated pest management (IPM) practices to control pests effectively.
Step 7: Final Touches and Testing
7.1 Safety and Accessibility
-
Ensure all pathways are clear and accessible for workers and equipment.
-
Install safety features such as handrails and non-slip flooring where necessary.
7.2 Testing and Calibration
-
Test all systems (heating, cooling, irrigation) to ensure they function correctly.
-
Calibrate sensors and controls for accurate climate regulation.
7.3 Training and Documentation
-
Train staff on operating and maintaining the greenhouse systems.
-
Keep detailed records of all installations, permits, and maintenance schedules.
Conclusion
Building a commercial greenhouse involves careful planning, precise execution, and ongoing maintenance. By following this step-by-step guide, you can create a productive and efficient greenhouse that meets your agricultural goals. Investing in quality materials and systems will ensure long-term success and profitability in your commercial growing venture.
Most Popular Greenhouse Articles